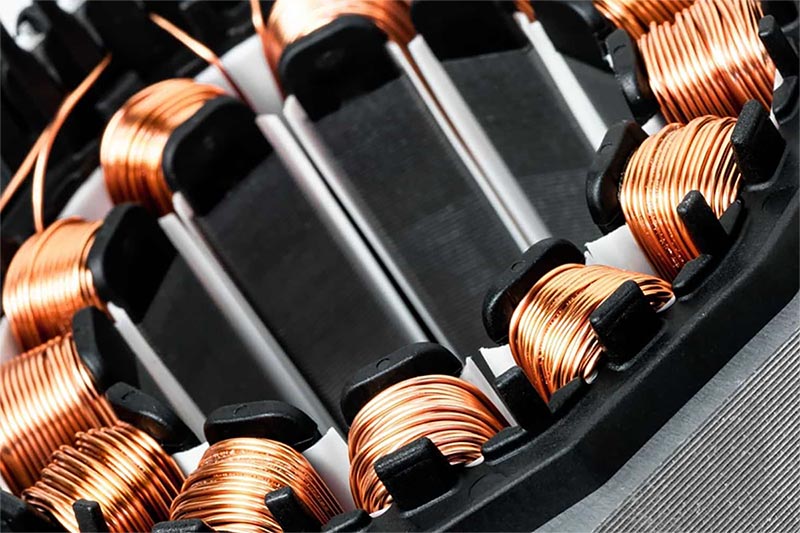
Stator Winding
- Our stator assembly offers flat and round copper wire winding, suitable for both small batches during the sample stage and large batches in later production. Flat wire is ideal for automatic production lines.
- This versatility supports generators and electric motors, offering reliable solutions for diverse energy needs.
- Various Winding Methods
- Stator Diameter Range: 50~500mm
- Pin Winding Range : 150~400mm
- Daily Production Capacity: 5-50 Sets
Stator Winding Process
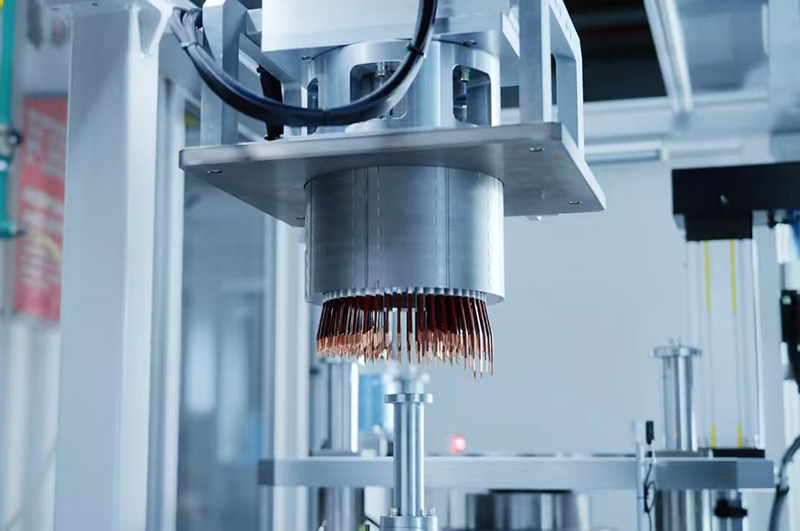

01. Wire Selection
02. Manual Winding
03. Welding & Shaping
04. Advanced Coating and Molding
05. Twisting and Laser Welding
06. Comprehensive Testing
Stator Winding Material Types
Round Copper Wire
- Standard for general motor winding applications.
- Offers good electrical conductivity and stability.
- Easy to handle and wind.
- Suitable for low-to-medium power motors.
Flat Copper Wire
- High slot fill rate for compact designs.
- Enhances efficiency with reduced copper loss.
- Ideal for high-performance motor applications.
- Better heat dissipation and performance.
Based on Winding Process
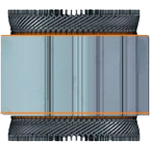
I-pin Winding
- Simple wire shape, straight “I” formation.
- Lower slot fill, suitable for smaller motors.
- Easy manufacturing and lower cost.
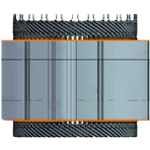
Hairpin Winding
- Bent wire shape resembling a hairpin.
- Higher slot fill, better efficiency.
- Ideal for medium to high-power motors.
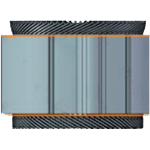
X-pin Winding
- Wire bent in an "X" shape.
- Maximizes slot fill and reduces losses.
- Used in high-performance, high-efficiency motors.
Based on Winding Arrangement
Concentrated Winding
- Coils are wound in closely packed groups.
- Shorter coil paths reduce copper losses.
- Lower manufacturing cost, easier to produce.
- Typically used in smaller, low-power motors.
Distributed Winding
- Coils spread across multiple stator slots.
- Improved efficiency and electromagnetic performance.
- Ideal for high-power, larger motors.
- Reduces harmonics and enhances motor stability.
Based on Connection Type
Star Connection
- Coils connected to a central point.
- Provides lower voltage and higher current.
- Common in high-voltage, low-power motors.
- Reduces starting current for smooth operation.
Delta Connection
- Coils form a triangular loop.
- Provides higher voltage and lower current.
- Ideal for low-voltage, high-power motors.
- Efficient at full-load operation.
Based on Coil Construction
Lap Winding
- Coils overlap to form a lap configuration.
- Simple, robust, and cost-effective construction.
- Suitable for low-speed, high-torque motors.
- Provides good mechanical strength and durability.
Wave Winding
- Coils arranged in a wave-like shape.
- Ideal for high-speed, high-efficiency motors.
- Reduces harmonics and enhances performance.
- Requires more turns for compact design.
Based on the Number of Phases

Single-Phase Winding
- Uses one-phase power for low-power motors.
- Simple design, lower cost and maintenance.
- Produces pulsating torque, less smooth operation.
- Common in household appliances and small fans.

Three-Phase Winding
- Uses three-phase power for higher efficiency.
- Provides smoother, continuous torque output.
- Common in industrial and large motors.
- Reduces motor size and improves performance.
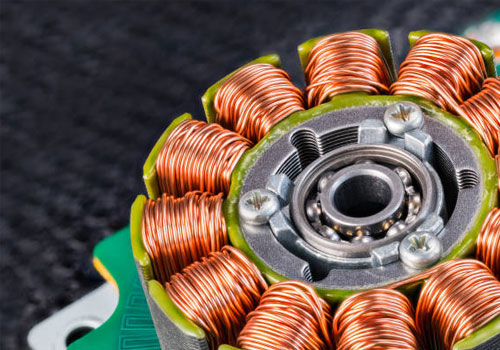
Multi-Phase Winding
- Uses more than three phases for power.
- Provides smoother torque with higher efficiency.
- Ideal for specialized industrial applications.
- Minimizes harmonics and enhances motor stability.
Based on Winding Layer
Single-Layer Winding
- One coil per slot, simple design.
- Fewer turns, compact and efficient.
- Used in low-power, low-voltage motors.
- Easier and cost-effective to manufacture.
Double-Layer Winding
- Two coils per slot, more complex.
- Higher efficiency with more turns per coil.
- Ideal for high-power, high-voltage motors.
- Provides better performance and stability.
Based on the Number of Poles
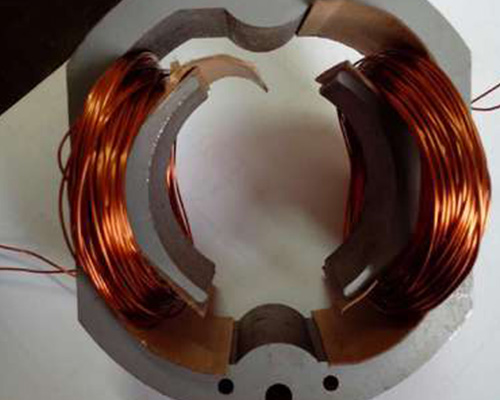

Two-Pole Windings
- High-speed operation, low torque.
- Common in small, lightweight motors.
- Suitable for appliances and fans.
- Simple design, higher efficiency.
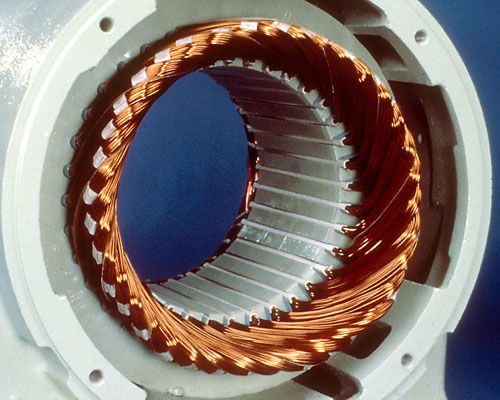
Four-Pole Windings
- Moderate speed and torque output.
- Common in industrial motors and pumps.
- Provides better torque than two-pole.
- Suitable for medium-speed applications.
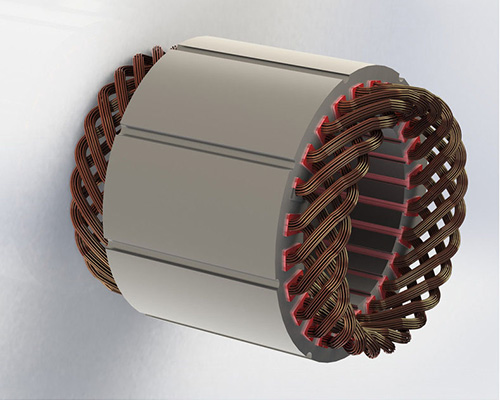
Six-Pole and More
- Low-speed, high-torque operation.
- Ideal for large, heavy-duty motors.
- Common in generators and high-load applications.
- Provides smoother operation with more poles.
Based on the Coil Pitch
Full-Pitch Winding
- Coil spans the entire pole pitch.
- Maximizes motor efficiency and performance.
- Reduces harmonic distortion and losses.
- Common in high-performance, large motors.
Short-Pitch Winding
- Coil spans less than full pole pitch.
- Reduces copper usage and motor size.
- Increases harmonic distortion and losses.
- Suitable for cost-effective, compact motors.
Based on Type of Current
AC Winding
- Used for alternating current motor applications.
- Alternating current flow through coils.
- Common in induction motors and transformers.
- Suitable for high-speed, low-torque motors.
DC Winding
- Used for direct current motor applications.
- Unidirectional current flow through coils.
- Common in small motors and generators.
- Suitable for low-speed, high-torque applications.
Stator Winding Applications
Stator winding applications are crucial in motors, generators, transformers, and electrical equipment, enhancing energy efficiency and operational reliability.
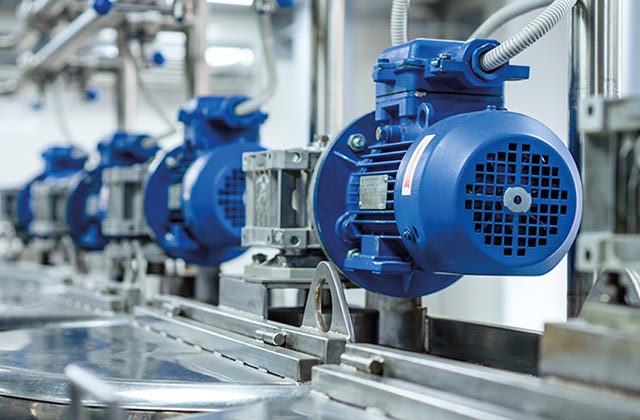

Electric Motors
Stator windings in induction, synchronous, and DC motors generate magnetic fields, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion for driving various devices and machinery.
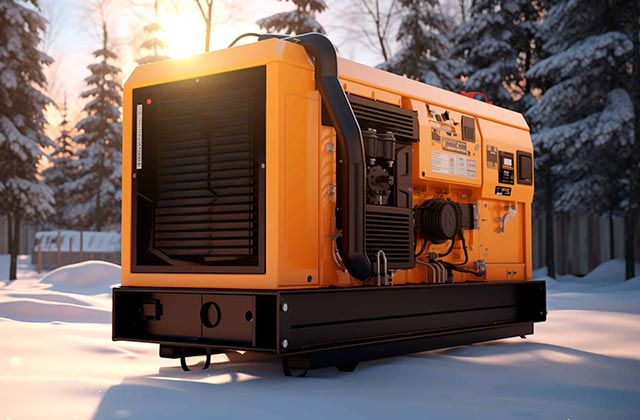

Generators
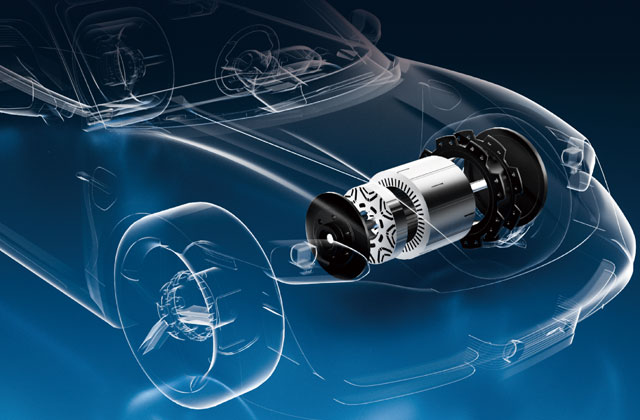

Electric Vehicles (EVs)

Industrial Equipment
Stator windings in motors drive industrial equipment, providing mechanical power for machines such as conveyors, pumps, and compressors essential in manufacturing processes.
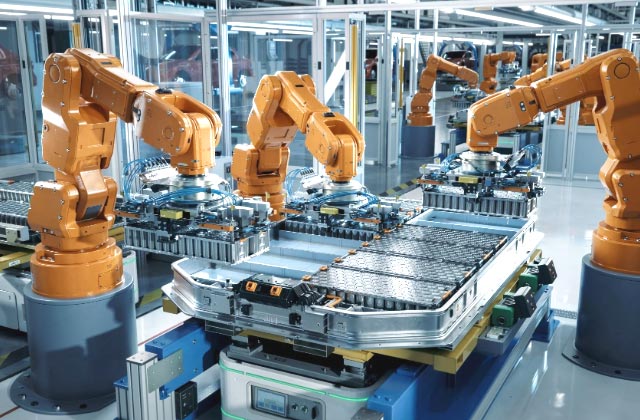

Robotics

HVAC Systems

Renewable Energy Systems
In wind and hydroelectric power generation, stator windings convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, crucial for harnessing renewable energy and supporting sustainable power grids.

Power Tools

Aerospace
General FAQs
How do you test the quality of stator windings?
Can stator windings be repaired or rewound?
How do you ensure winding consistency in mass production?
Can stator windings be customized for specific applications?
What is the role of insulation in stator windings?
Insulation prevents short circuits, electrical leakage, and ensures safety. It also helps maintain efficient motor operation by protecting windings from moisture, heat, and other environmental factors.


