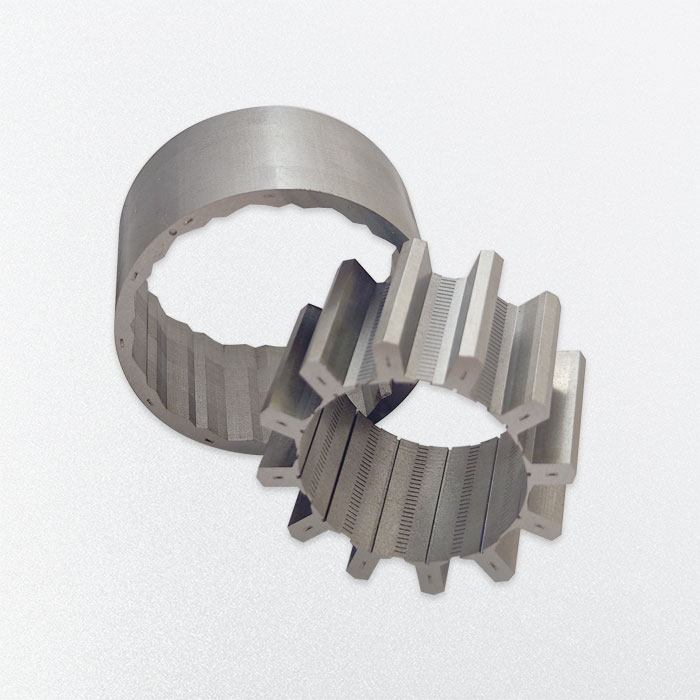
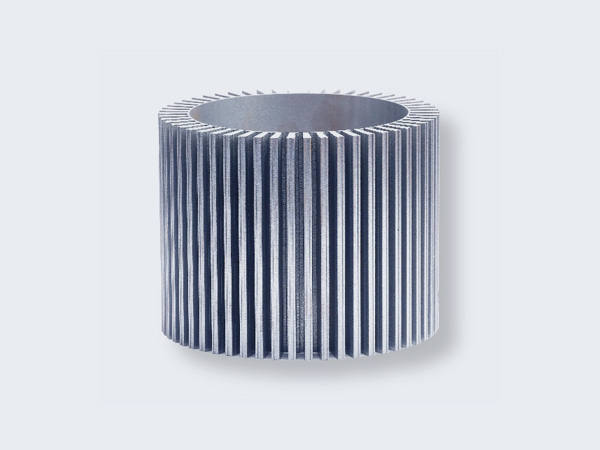
Stator & Rotor Lamination Stacks Manufacturer
- Lamination to stacking is crucial in core manufacturing, ensuring precise alignment, reduced eddy current losses, and optimal magnetic properties.
- We review the tolerances and offer design advice on the stator and rotor stacking process, based on the thickness of each piece, stack length, and overall design.
- Realize Batch Production of In-Mold Glue Dispensing
- Various Automatic Lines and Manual Stacking Processes
- 32 Sets Punching Machine From 80T~650T
- Customization for Diverse Applications
- Certificate: IATF16949
Our Stacking Processes
Our laminations are assembled into core stacks using methods like riveting, interlocking, welding, self-adhesion (backlack), gluing, bolting, and buckling. When the stator or rotor lamination length is too high, two processes may be used together.

In-Mold Glue Dispensing
- Dispensing solution completed inside the mold.
- Glue solidifies within 10-20 seconds.
- High interchip strength.
- Excellent performance parameters.
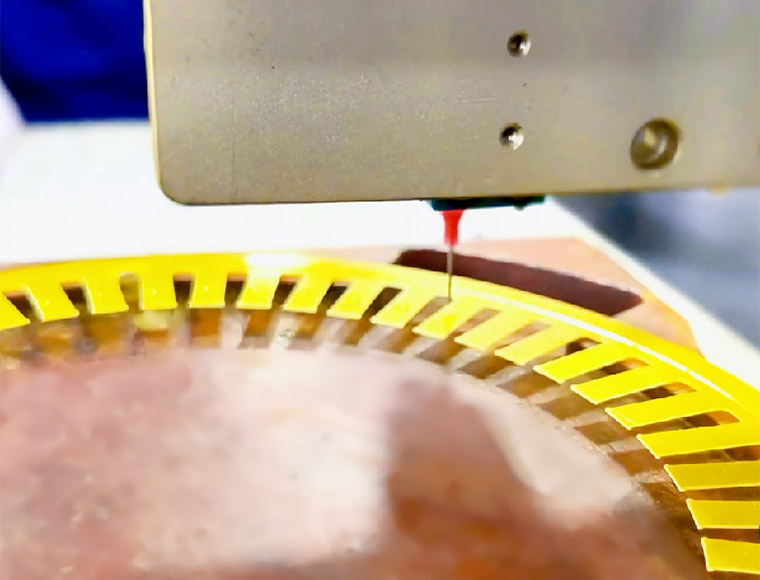
Out-Mold Glue Dispensing
- Applied outside the mold.
- Visual automatic positioning system combined with the injection valve needle cylinder dispensing.
- Tilt or 360-degree rotation dispensing.
- Self-adhesive coating heating scheme.
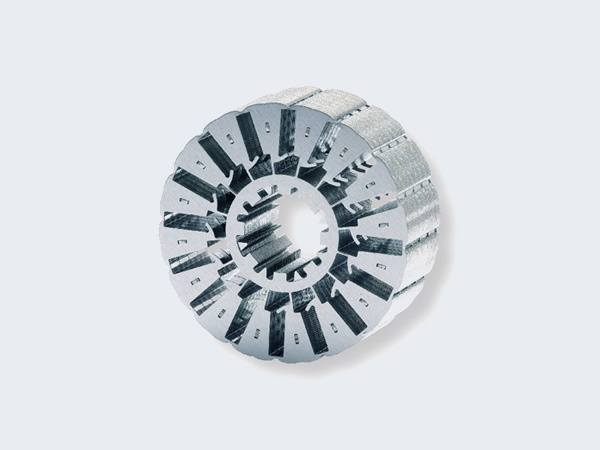

Progressive Mold Self-Interlocking Stacking
- Automatically completes interlocking during stamping.
- Efficient for high-volume production.
- Rectangular or round interlock points.
- Works for rotor and stator laminations.
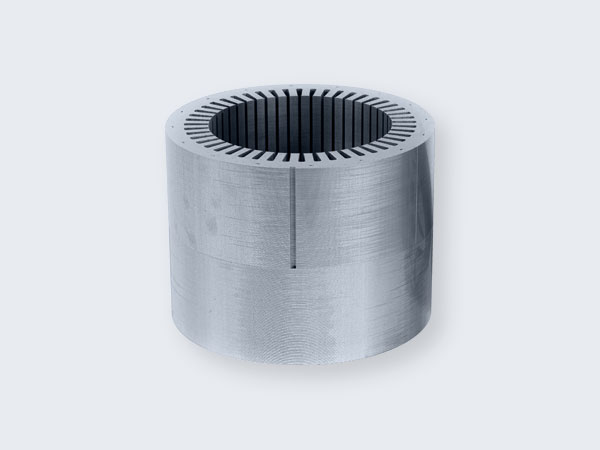

Compound Mold Single Punch Self- Interlocking Stacking
- Secures interlock at specific points.
- Ideal for smaller batches or customized parts verification.
- Flexible process with human intervention.
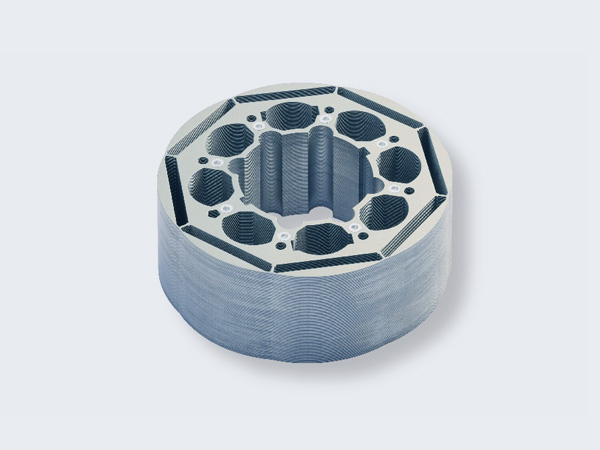

Rivet Stacking
- Use head or flat rivets.
- Ensures durable connection and secure assembly.
- Suitable for rotor laminations.
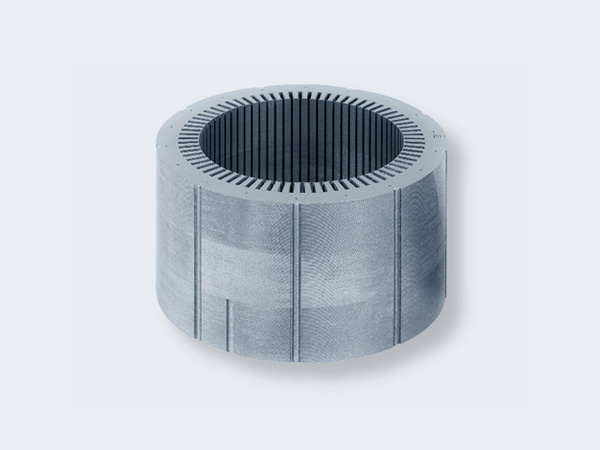

Welding Stacking
- Laser, TIG, galvanometer welding methods.
- Ensures strong bond, minimal distortion.
- Best for high precision stator laminations.
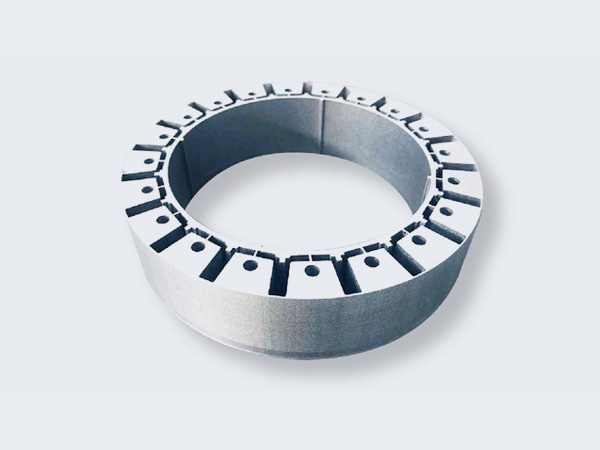

Self-Adhesive Stacking
- B35A300-Z/B50A400-Z etc. Heat Adhesives.
- Smooth finish, strong bonding, durable.
- Ideal for advanced heat-activated coatings.
- Works for rotor and stator laminations.
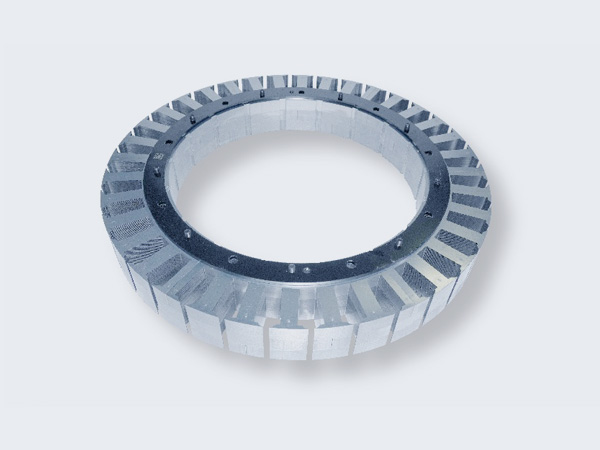
Bolt Stacking
- Assemble large-diameter stator laminations.
- Offers adjustability, stability, and reusability.
- Great for large motors with robust connections.
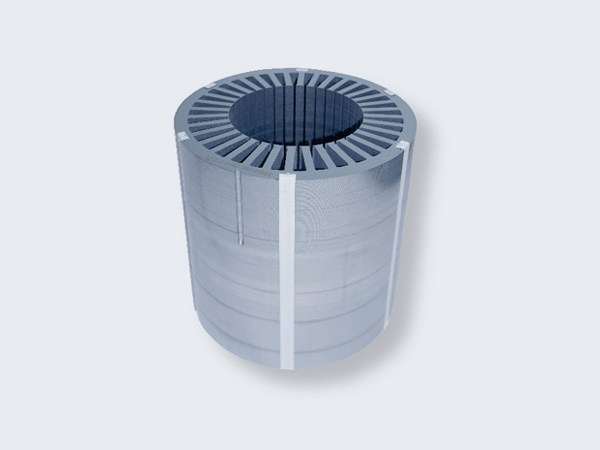

Buckle or Clamping Stacking
- Straight or oblique buckles.
- Quick assembly, robust design.
- Best for compact stator lamination.
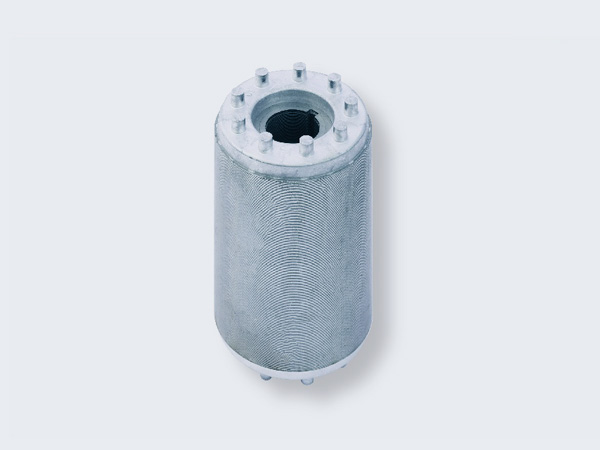

Al-casting or Cu-casting Stacking
- Both single lamination and stacking can be casting pressed.
- Equipped with horizontal and vertical aluminum casting equipment to meet different outer diameter and height requirements.
- Best for compact rotor lamination.
Stacking Process Steps
After producing the stator and rotor laminations, the assembly and fixation of their lamination stacks typically follow these nine common steps:
01. Prepare Laminations
02. Laminations Alignment
03. Selection Stacking Method
04. Stacking the Laminations
05. Compression and Clamping
06. Securing the Stack
07. Dimensional and Geometric Inspection
08. Post-Processing (Optional)
09. Final Quality Inspection
Post-Stacks Processing
We utilize various processes to enhance the structural integrity, performance, and longevity of laminated stator and rotor core stacks, ensuring optimal functionality.
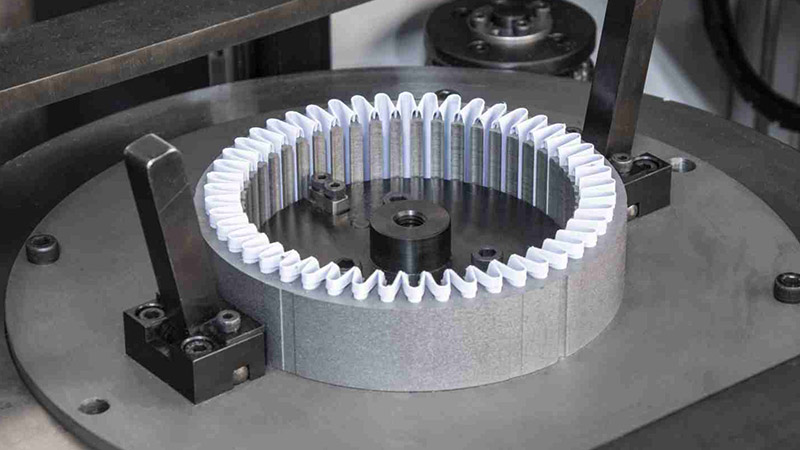
01. Insulation
02. Resin Curing
03. Plating Coating
04. Vibration Damping
05. Heat Treatment
06. Magnetic Treatment
07. Laser Marking
08. Surface Grinding or Polishing
Grinding wheels are used to remove rough edges and surface defects, improving the smoothness and finish of laminated stacks, enhancing efficiency and appearance.
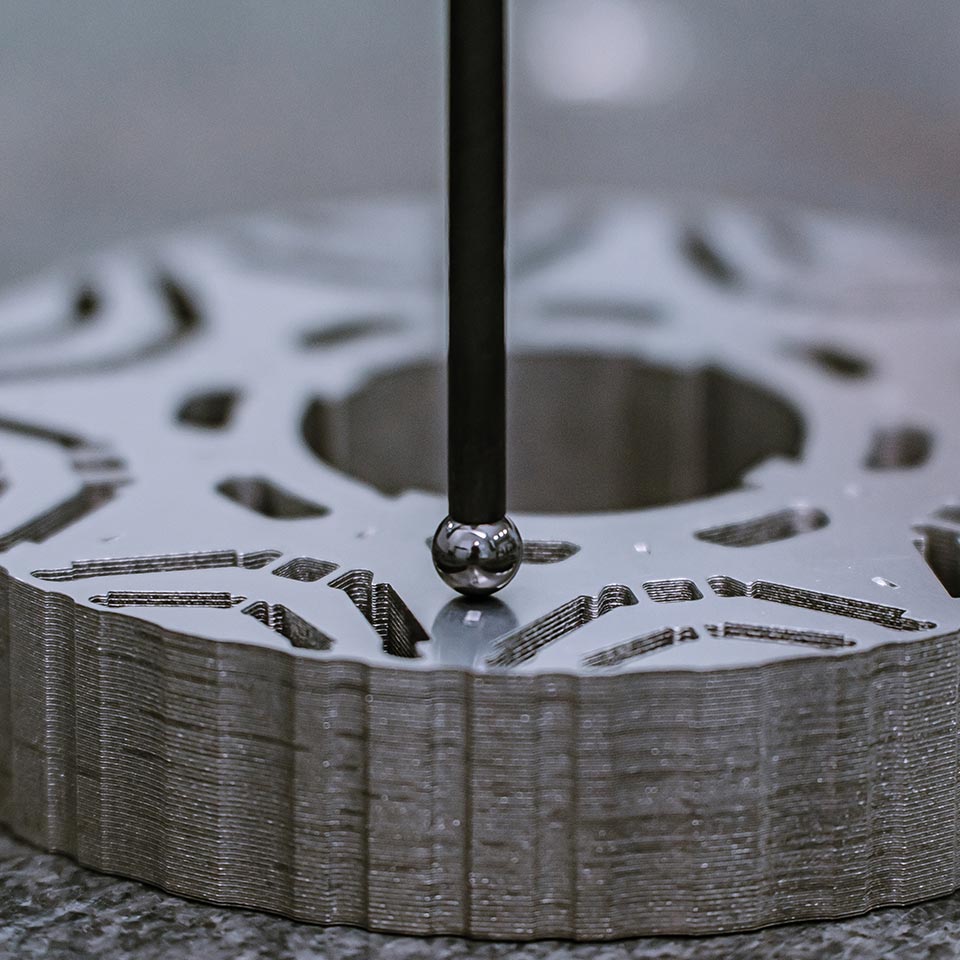
Final Quality Inspection
After post-processing, we conduct a comprehensive final quality inspection on our electric motor lamination stacks to ensure they meet all functional, safety, and performance standards.
- Visual Inspection
- Dimensional Measurement
- Magnetic Testing
- Electrical Insulation Testing
- Torque Testing
- Heat Resistance Test
- Vibration Test
- Mechanical Strength Testing
- Leakage Current Test


